Bariatric Surgery or GLP-1 medication: The Science-backed decision guide

Making a decision about significant weight loss is one of the most important health choices you can make. The options can feel overwhelming, pitting a permanent surgical solution against powerful new medications: Bariatric surgery or GLP-1 medication?
Our goal here is to provide a comprehensive, evidence-based comparison of all three primary pathways: bariatric surgery, FDA-approved GLP-1 drugs, and compounded semaglutide. We’ll cover the science, the real-world costs, and the day-to-day impact to empower you to have a truly informed conversation with your doctor.
What are the key differences between Bariatric surgery and GLP-1 medication
What Is Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric surgery is a medical procedure that physically changes the size or shape of your stomach and, in some cases, your small intestine to help you lose weight. It works by restricting the amount of food you can eat and, depending on the procedure, by altering how your body absorbs calories and sends hunger signals to your brain.
What are FDA-Approved GLP-1 Medications Like Ozempic and Wegovy?
FDA-approved GLP-1 medications are prescription drugs that you inject to help manage blood sugar and cause weight loss. They work by mimicking a natural gut hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which helps regulate your appetite and digestion. Wegovy is specifically approved for weight loss, while Ozempic is approved for type 2 diabetes but is often used “off-label” for weight management.
What is compounded semaglutide and how is it different from the Brand Names?
Compounded semaglutide is a version of the active ingredient in Ozempic and Wegovy that is prepared by a special kind of pharmacy called a compounding pharmacy. It is not the same as the FDA-approved, pre-packaged pens from the manufacturer. However the active ingredients have the same properties as the brand names.
Patients often choose this route because it is significantly more affordable and accessible, especially when the brand-name drugs are in shortage or not covered by insurance.
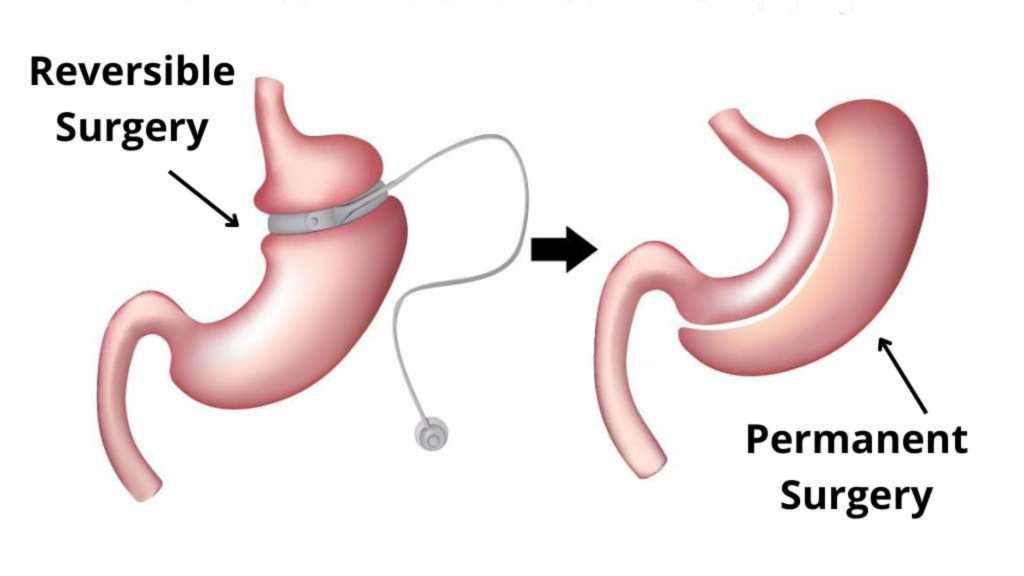
What are the main types of Bariatric Surgery?
The two most common types of bariatric surgery work in slightly different ways.
- What is a Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG)?
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy procedure removes about 70-80% of your stomach, leaving behind a smaller, banana-shaped “sleeve.” This physically limits how much food you can eat at one time. - What is a Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)?
The RYGB surgery creates a small stomach pouch and then connects it directly to a lower part of the small intestine. This both restricts food intake and reduces the calories and nutrients your body can absorb.
What Are the Different Types of GLP-1 Drugs Available?
While many GLP-1 drugs exist, they are built around a few key active ingredients.
| Drug Name | Active Ingredient | Primary FDA Approval | Key Feature |
| Wegovy | Semaglutide | Weight Management | Higher dose of semaglutide for weight loss |
| Ozempic | Semaglutide | Type 2 Diabetes | Lower dose of semaglutide |
| Mounjaro | Tirzepatide | Type 2 Diabetes | A “dual-agonist” that targets two hormones |
| Zepbound | Tirzepatide | Weight Management | Higher dose of tirzepatide for weight loss. |
How do these treatments cause weight loss?
How does Bariatric Surgery help you lose weight?
Bariatric surgery causes weight loss through a combination of physical and hormonal changes.
- How does surgery physically restrict food intake and alter gut hormones?
By reducing the size of your stomach, the surgery physically limits the amount of food you can comfortably eat. In medical terms, this also alters the secretion of gut hormones. For example, levels of ghrelin, the “hunger hormone,” often decrease significantly, reducing your appetite. - What role does the gut microbiome play after bariatric surgery?
Research suggests that surgery also changes the composition of the bacteria in your gut. This shift in the gut microbiome may contribute to improved metabolism and overall health, though the exact mechanisms are still being studied [External Link: Gut Microbiome Research].
How does GLP-1 Medications work?
GLP-1 medications work by hijacking your body’s natural appetite control system.
- How does semaglutide (in all forms) mimic natural hormones to reduce appetite?
The drug binds to GLP-1 receptors in your brain, telling it you are full and satisfied. This reduces food “chatter” and cravings, leading you to eat less without feeling deprived. - How do these drugs slow down stomach emptying to make you feel full?
GLP-1s also slow the rate at which your stomach empties its contents into the small intestine. This process, called delayed gastric emptying, means you feel physically fuller for longer after a meal.
Why Are Some GLP-1s (like Mounjaro) Called “Dual-Agonists”?
Some newer drugs like Mounjaro and Zepbound are called “dual-agonists” because they target two different hormone receptors: GLP-1 and GIP. By activating both pathways, these medications may lead to even greater weight loss and blood sugar control compared to those that only target GLP-1.
Why Are GLP-1 Injections Not Effective for Everybody?
GLP-1 injections may not be effective for everyone due to individual differences in genetics, metabolism, and the root causes of their obesity. Some people may be less sensitive to the medication’s effects or may not be able to tolerate the side effects long enough to see significant results.
How much weight can I expect to lose?
How Much Weight Do Patients Lose with Bariatric Surgery?
Patients who undergo bariatric surgery typically lose the most weight, often 50% to 70% of their excess body weight within the first two years. The results are generally durable, with many patients maintaining a significant portion of their weight loss long-term.
How much weight can you lose on GLP-1 Drugs?
On high-dose, brand-name GLP-1s, patients can expect to lose an average of 15% to 22% of their total body weight over the course of about a year. For a 200-pound person, this translates to a loss of 30 to 44 pounds.
The weight loss from compounded semaglutide should be similar to brand-name versions if the active ingredient is pure and the dosage is accurate.
Which treatment offers the most significant and permanent weight loss?
Bariatric surgery offers the most significant and permanent weight loss for the majority of patients. While GLP-1s are highly effective, their benefit is tied to continuous use, whereas surgery provides a permanent physical tool for weight management. However, GLP-1, particularly compounded semaglutide provide a more cost effective solution for weight loss.
Bariatric surgery or GLP-1: who is an ideal candidate for each treatment?
What Are the Official Qualifications for Bariatric Surgery (BMI & Health Conditions)?
You typically qualify for bariatric surgery if you have:
- A Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher.
- A BMI of 35-39.9 along with a serious obesity-related health condition, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or severe sleep apnea.
What Are the Qualifications for a Prescription for GLP-1?
You generally qualify for a brand-name GLP-1 for weight loss if you have:
- A BMI of 30 or higher.
- A BMI of 27-29.9 with at least one weight-related health condition.
Who typically chooses compounded Semaglutide as an option?
People often choose compounded semaglutide when they meet the clinical criteria for the medication but cannot get it due to cost, lack of insurance coverage, or shortages of the brand-name drugs. It is a more accessible and affordable pathway for many qualified individuals.
How do you choose based on your health goals and lifestyle?
Choosing the right option depends on your individual needs, and this table can help guide your thinking.
| Consideration | Bariatric Surgery | Brand-Name GLP-1s | Compounded GLP-1s |
| Need to lose >100 lbs | ✅ | ⚠️ | ⚠️ |
| Prefer a non-invasive approach | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Want an FDA-approved treatment | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Cost is my primary concern | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Want to avoid lifelong medication | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Concerned about permanent changes | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
What are the health benefits beyond weight loss?
Which Treatment Is Most Effective for Reversing Type 2 Diabetes?
Bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment for reversing type 2 diabetes. Many patients experience remission within days or weeks of the procedure, often before significant weight loss has even occurred, due to the profound hormonal changes.
How Do These Options Affect Heart Health and Blood Pressure?
All three options can significantly improve heart health by lowering blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. The dramatic weight loss from surgery often leads to the most substantial improvements. However, GLP-1 medication have also been shown in studies to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events.
H3: Can These Treatments Improve Conditions Like Sleep Apnea and Fatty Liver Disease?
Yes, significant weight loss from any of these methods can lead to dramatic improvements or even resolution of conditions like obstructive sleep apnea and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
H3: How Does Each Option Impact Overall Quality of Life and Mental Health?
Most patients report a substantial improvement in their quality of life, including better mobility, mood, and self-esteem. While the journey has its own challenges, achieving significant weight loss is often life-changing for physical and mental well-being.
What Are the Safety Profiles, Side Effects, and Long-Term Risks?
TL;DR All options have risks. Surgery involves immediate and long-term surgical complications and nutritional deficiencies. GLP-1s (both types) primarily cause gastrointestinal side effects.
What Are the Immediate Surgical Risks of Bariatric Procedures?
The immediate risks of bariatric surgery are similar to any major operation. These can include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Blood clots
- Anesthesia-related complications
- Leaks from the staple lines in the stomach or intestine
What Are the Long-Term Complications of Bariatric Surgery?
Long-term complications from surgery require lifelong monitoring.
- What is “Dumping Syndrome” and how is it managed?
This occurs when food, especially sugar, moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, causing symptoms like nausea, cramping, and dizziness. It’s managed by carefully modifying your diet. - What are the symptoms if you fail to take your required vitamins?
Failing to take prescribed supplements can lead to serious nutritional deficiencies. Symptoms can include severe fatigue (iron/B12 deficiency), bone pain (calcium/vitamin D deficiency), and neurological problems.
What Is the connection between Bariatric Surgery and Alcohol use disorder?
Some studies suggest that patients, particularly after gastric bypass, may be at an increased risk for developing alcohol use disorder. This is because changes in alcohol metabolism can lead to feeling the effects of alcohol much faster and more intensely.
What Are the Most Common Side Effects of GLP-1 medication?
The most common side effects are gastrointestinal and tend to be most pronounced when starting the medication or increasing the dose.
- What are the practical, day-to-day strategies for managing these side effects?
To manage side effects, providers often recommend:- Eating smaller, more frequent meals.
- Avoiding greasy or very sweet foods.
- Staying well-hydrated with water.
- Eating slowly and stopping when you feel satisfied, not “stuffed.”
What Are the Serious risks of GLP-1 medication?
In rare cases, GLP-1s have been associated with more serious risks, including pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), gallbladder problems, and a risk of a specific type of thyroid tumor. You should discuss your personal and family medical history with your doctor.
Less known benefits of GLP-1 medication
While it is not an approved use, a significant number of users anecdotally report that GLP-1 medications reduce their desire for addictive substances and curb compulsive behaviors. It’s crucial to understand that this is an area of active scientific investigation, and these drugs are not prescribed as addiction treatments.
The reported effects that researchers are now formally studying in clinical trials include reduced cravings for:
- Alcohol: Many users report drinking significantly less because the “buzz” or pleasure from alcohol feels muted.
- Nicotine: Some people find they have a reduced desire to smoke or vape while on the medication.
- Cannabis: Similar to alcohol, the rewarding sensation may be lessened.
- Other Compulsive Behaviors: Anecdotal reports also mention a decreased urge for activities like compulsive shopping, gambling, or skin picking.
Scientists believe this is directly linked to the drug’s effect on the brain’s dopamine reward system, making these once-pleasurable activities feel less satisfying and therefore less compelling. Large-scale studies are currently underway to confirm these effects and understand their potential therapeutic use in the future
What Happens If You Stop Treatment?
Will I regain weight after stopping any form of GLP-1 medication?
Yes, you will likely regain a big share of the weight you lost after stopping a GLP-1 medication. These drugs manage weight; they do not cure the underlying biology of obesity. They are intended for long-term use. However, that’s why it’s recommended to pair GLP-1 medication with psychological and nutritional support, diet and behavioral changes for long term support. Professional telehealth providers give you access to quality all-around support for your weight loss journey.
Do You Gain the Weight Back Years After Bariatric Surgery?
Some weight regain (about 10-15%) is common several years after surgery, but most patients maintain a significant amount of their initial weight loss long-term.
- Why does weight regain happen after surgery and what are the strategies to manage it?
Regain can happen due to the stomach pouch stretching slightly over time or a return to old eating habits. Strategies to manage it include adhering to the post-surgical diet, regular exercise, and seeking support from your bariatric team.
How Much Do These Three Options Cost?
TL;DR Surgery has the highest upfront cost but may be covered by insurance and has fewer ongoing expenses. Brand-name GLP-1s have a high monthly cost that relies on insurance coverage. Compounded GLP-1s are the cheapest monthly option and do not require insurance. You can find GLP-1 providers in your state that covers both compounded and branded options through www.glp-finder.com
What Is the upfront cost of Bariatric Surgery?
Without insurance, bariatric surgery typically costs between $20,000 and $30,000 in the United States. This price usually includes the surgeon’s fees, hospital facility fees, and anesthesia.
How Much Does Wegovy or Ozempic Cost Per Month Without Insurance?
Without insurance, the list price for brand-name GLP-1s is typically between $1,000 and $1,400 per month.
Why Is Compounded Semaglutide a Cheaper, No-Insurance-Needed Option?
Compounded semaglutide is cheaper because compounding pharmacies can acquire the raw pharmaceutical ingredient and prepare it in-house, avoiding the research, development, branding, and marketing costs of major pharmaceutical companies. This allows them to offer it for a cash price, often between $150 and $300 per month. They also provide 24/7 support from licensed health practitioners and nutritionists.
Will Insurance Cover Bariatric Surgery or Brand-Name GLP-1s for Weight Loss?
Many insurance plans cover bariatric surgery if you meet the medical necessity criteria. Coverage for brand-name GLP-1s for weight loss is less consistent and depends heavily on your specific plan’s formulary for anti-obesity medications. Insurance does not cover compounded medications.
Which Option Is Most Cost-Effective Over a Lifetime?
This is a complex question. If covered by insurance, bariatric surgery may be most cost-effective due to its one-time cost and potential to reduce other healthcare expenses. For those paying out-of-pocket, compounded semaglutide is the most affordable ongoing treatment, while brand-name drugs are the most expensive long-term.
What Will Your Daily Life Actually Be Like?
What Does the Post-Surgery Diet and Lifestyle Look Like After 5 or 10 Years?
Years after surgery, your daily life involves a permanent commitment to:
- Eating very small, protein-focused meals.
- Avoiding high-sugar and high-fat foods to prevent dumping syndrome.
- Taking a specific regimen of vitamins and minerals every day.
- Regular medical follow-ups to monitor for nutritional deficiencies.
What Is the Day-to-Day Reality of Taking Weekly GLP-1 Injections?
Daily life on a GLP-1 involves managing your appetite and side effects. You’ll likely find you have significantly reduced interest in food. The day-to-day reality is a weekly, quick-and-easy injection and being mindful of your diet to minimize potential side effects like nausea.
What Are the Common Psychological Challenges After Massive Weight Loss from Surgery?
Patients may face unexpected psychological challenges. These can include dealing with loose or excess skin, navigating changes in social relationships, and adjusting to a new body image that can sometimes feel unfamiliar.
Can Bariatric Surgery and GLP-1s Be Used Together?
Can You Use GLP-1s to Lose Weight Before Surgery to Reduce Risk?
Yes, surgeons sometimes prescribe GLP-1s for several months before bariatric surgery. This can help patients lose 10-15% of their body weight, which can make the surgery itself safer and technically easier to perform.
Can You Use GLP-1s After Surgery to Address a Weight Loss Plateau?
Yes, this is becoming a more common strategy. If a patient experiences a weight loss plateau or some weight regain years after surgery, adding a GLP-1 medication can help restart weight loss and improve metabolic health.
What Are the Benefits and Risks of Combining These Two Approaches?
The primary benefit is achieving greater overall weight loss than either method could alone. The risks are generally the same as using each treatment individually, but your medical team will need to carefully monitor you for side effects and nutritional status.
What Does the Future of Obesity Treatment Look Like?
Are There New Drugs Coming That Are Better Than Ozempic or Wegovy?
Yes, the pipeline for new anti-obesity medications is very active. Researchers are developing “triple-agonist” drugs that target three different hormones (GLP-1, GIP, and Glucagon), which may lead to even more significant weight loss in the future.
Are There Less Invasive Surgical Options Being Developed?
Yes, less invasive options are gaining traction. These include endoscopic procedures like the endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG), where a surgeon uses stitches to reduce the stomach’s size via a tube passed through the mouth, requiring no external incisions.
How Do You Start the Conversation With Your Doctor?
What Questions Should You Ask Your Doctor to Decide Which is Right for You?
To make the best decision, you need to be an active participant in the conversation. Go to your appointment prepared to ask:
- Based on my specific health profile, what are the biggest risks and benefits of each option for me?
- What does success look like for each option, and what is a realistic outcome for someone like me?
- What are the total expected costs, both with and without my insurance?
- What kind of long-term support and follow-up care do you provide for each path?
- If considering compounded medication, can you help me find a reputable and accredited U.S. compounding pharmacy?
What Tests and Evaluations Are Required Before Starting Any Treatment?
Before starting any treatment, you can expect a comprehensive evaluation. This typically includes blood work, a review of your medical history, a physical exam, and often a psychological evaluation to ensure you are prepared for the lifelong changes required.
What Is the Role of a Multidisciplinary Team (Surgeon, Dietitian, Psychologist)?
Successful long-term weight management, especially with surgery, relies on a team approach. A surgeon performs the procedure, a dietitian guides your nutritional changes, and a psychologist provides support for the behavioral and emotional adjustments you’ll need to make. This team works together to support you through your journey.
Conclusion: Making Your Informed Choice
Navigating the choice between bariatric surgery and a GLP-1 medication is a deeply personal process, and the right path is a unique one for every individual. As we’ve covered, there is no universal “winner.” Bariatric surgery offers a powerful, permanent tool for profound physical and metabolic change, demanding a lifelong commitment to a new way of life. Brand-name and compounded GLP-1s provide a revolutionary, flexible approach to managing the biology of hunger, requiring ongoing use to maintain their remarkable benefits.
Ultimately, this guide is designed to be your launchpad for the most critical step: a comprehensive conversation with a qualified healthcare provider. They are the only ones who can take this information and apply it to your specific health profile, goals, and lifestyle.
For many, especially those leaning towards exploring GLP-1 medications like Ozempic, Wegovy, or the more accessible compounded semaglutide, the question becomes: “What’s the best way to have that conversation?”
This is where modern telehealth services have become an invaluable resource. They offer a direct, convenient, and specialized pathway to connect with doctors who are experts in the nuances of medical weight management. An online consultation allows you to discuss your unique health profile from the comfort of your home, understand your eligibility without a long wait for an appointment, and explore all your options—from navigating insurance for brand-name drugs to understanding the process for compounded medications.
If you feel a GLP-1 medication aligns with the goals you’ve identified on this journey, a telehealth consultation can be the most efficient and informed way to move forward.